Solutions
-
10 % or less
combustion rate at furnace throa
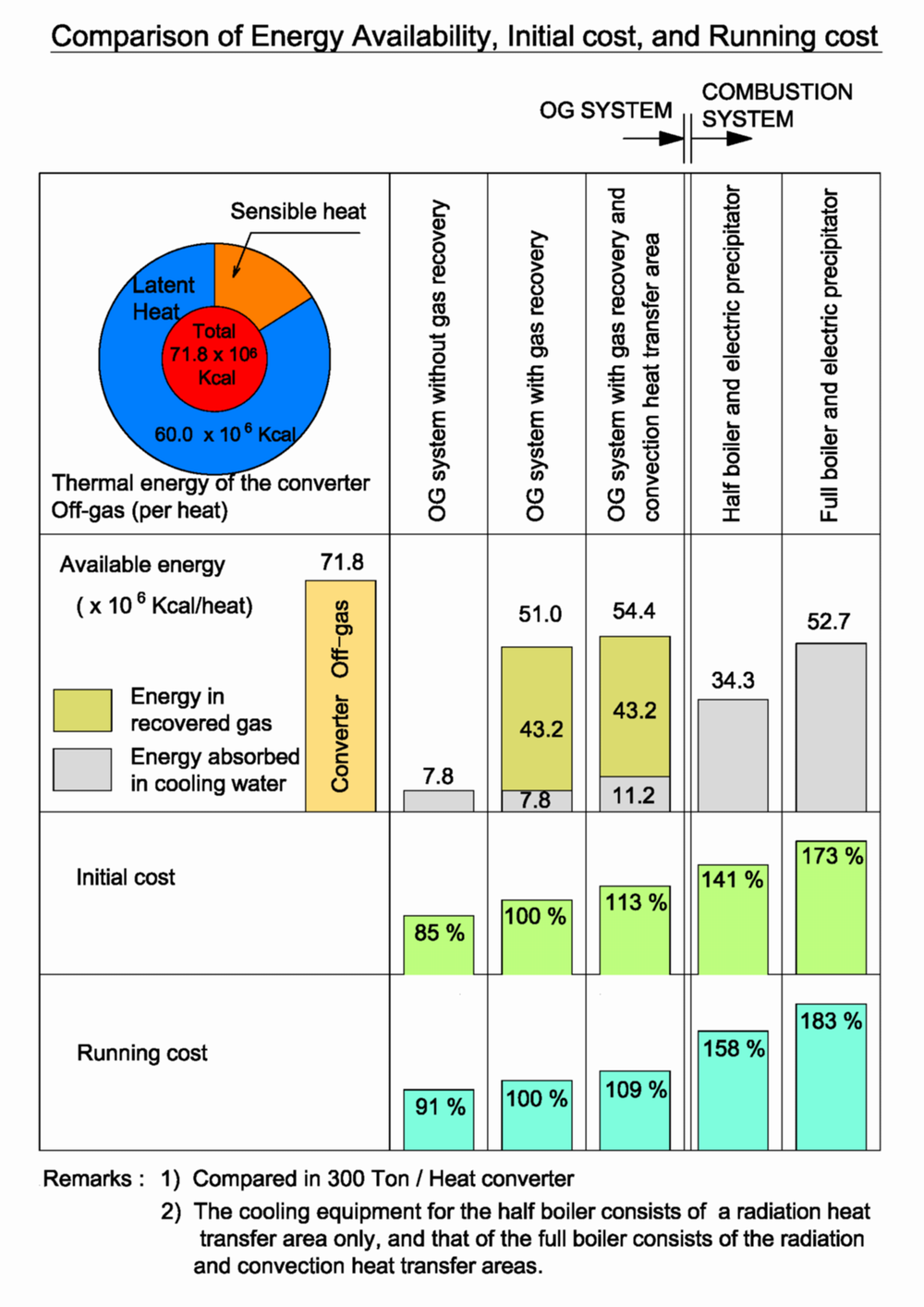
Reduction of Production Cost
The Hood pressure contol system of OG can ensure to suppress combustion rate of LD gas down to 5 -10%, by automatic control of the Ring Slit Washer (RSW) being also fucntioned as key part(s) of the Dust collecting system of OG.
This system leads to minimize LD-gas flow rate throughout converter’s operations, that surely makes it possible to get much more compact facilities compared with the system of full-combustion type. Therefore, the key components such as IDFan, pumps can also be minimized so that cost-saving can be certainly achieved more in terms not only of their initial investment but also of their electrical power consumption.
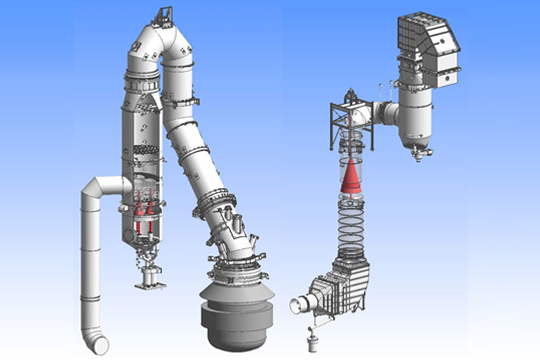
Customization
The compact facility of OG system featuring suppressed combustion type ensures you to provide more flexible design, compared with others of full-comnustion type.
The compact facility and its high-flexibility of design of OG surely can correspond to any site-condition fully well enough for your needs especially for revamping projects.

Environmental Friendliness
-
70~100 ㎥N/t-steel
(at 2000kcal/㎥N)Basic unit of recovered gas
-
70~100 kg/t-steel
Basic unit of recovered steam
-
30~50 mg/㎥N
(at flare stack outlet)Dust-collection performance
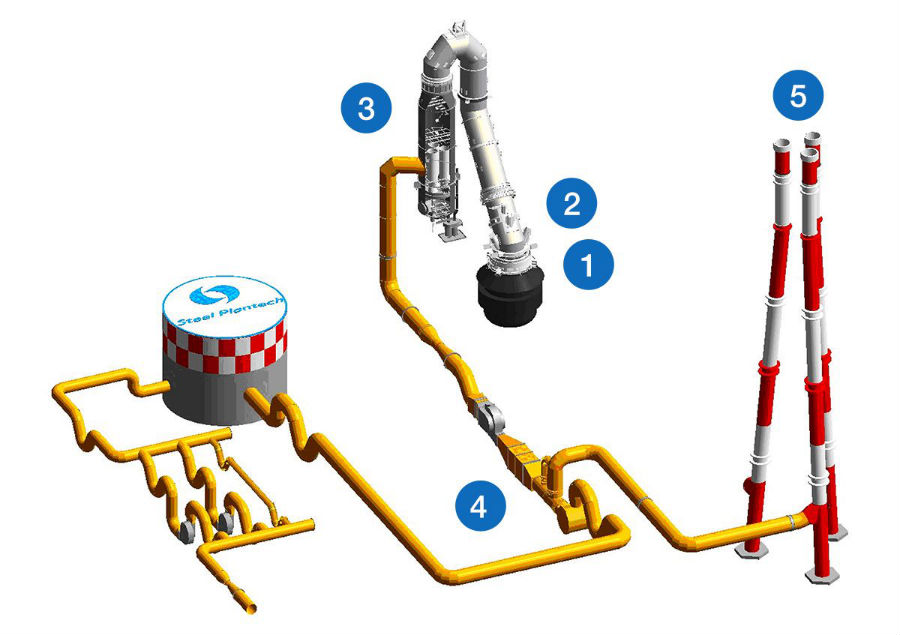
- 1The venturi scrubber-type Ring Slit Washer (RSW), being as the key part(s) of the 2nd stage dust collecting system of OG, allows superior dust collection efficiency to be maintained even when amount of LD-gas fluctuates during blowing.
- 2All the inside surfaces of Gas duct of OG keeps fully-wet as always so that there is no iginition source at all, that surely ensure you to keep positive safety throughout converter’s operations.
- 3Not only LD-gas recovery with high density of CO, steam generation by boiler system can be simultaneously achieved by OG. Also our unique technologies of installing convection heat transfer part(s) additionally can give you more amount of steam.